NAIROBI, Aug 07 (IPS) – Local weather change-related excessive climate jeopardizes Kenya’s improvement agenda; though it contributes little or no to international warming, it’s marked as a high-risk nation by improvement banks.Kenya contributes lower than 0.1 p.c of worldwide greenhouse gasoline emissions yearly, but improvement banks have flagged the East African nation as a excessive local weather danger. This is because of excessive climate adjustments which might be more and more threatening the nation’s improvement agenda, widening socio-economic inequalities, and deepening rural poverty and starvation.
Local weather change is a long-term shift in temperatures and climate patterns. Local weather danger is the potential hurt brought on by local weather change, comparable to monetary, social, and environmental destruction and lack of life. Nation-specific local weather danger profiles are a abstract of an evaluation of local weather tendencies over an extended time period, revealing how variability in climate patterns impacts life and livelihoods.
International locations are suggested to make use of these profiles to tell their improvement agenda, as failure to take action can considerably derail achievement of set improvement objectives. As an example, unpredictability in climate patterns has a unfavourable affect on sure sectors of Kenya’s economic system.
This consists of agriculture, tourism, horticulture, livestock and pastoralism, and forest merchandise. Almost 98 p.c of agriculture is rain fed. Utilizing local weather danger projections, the nation can spend money on irrigation to cut back the affect of local weather change on the sector, as roughly 75 p.c of Kenyans draw their livelihood from agriculture.
Kenya’s most up-to-date local weather danger profile offers a climatic development abstract spanning twenty years from 1991 to 2020, revealing that an estimated 68 p.c of pure disasters in Kenya are brought on by excessive climatic occasions, principally floods and droughts. The remaining 32 p.c represents illness epidemic.

Excessive Temperatures Inflicting Frequent, Intense Droughts
General, 16 drought occasions are on file from 1991 to 2020, affecting tens of millions of individuals and inflicting an general estimated harm of USD 1.5 billion. Regardless of floods being a more moderen phenomenon in Kenya they’re turning into more and more frequent, leading to 45 flood occasions throughout the similar interval. Whereas a sample of droughts started to emerge way back to 1975, a sample of floods has solely begun to emerge from 2012 to 2020.
A repeating sample of droughts and floods prices the nation roughly 3 to five p.c of its annual Gross Home Product. Over the previous twenty years, Kenya’s imply annual temperature was 24.2 diploma Celsius—with a excessive of 30.3 diploma Celsius and a low of 18.3 diploma Celsius.
To present a perspective of common temperatures in Kenya, 2023 was the most popular 12 months on file and 2024 is following the development. In line with the Affiliate Professor, Meteorology, College of Nairobi writing in The Dialog the capital Nairobi common temperatures fare usually reasonable, between 24°C and 25°C on the upper aspect and 17°C-18°C on the decrease aspect.
“These are typically very snug temperatures. Nevertheless, within the December-January-February interval, most temperatures are usually excessive, ranging between 26°C and 27°C.
“This 12 months, temperatures in February went as much as between 29°C and 30°C, even hitting 31°C. That is about 6°C increased than regular Nairobi temperatures. That could be a massive distinction and our our bodies are certain to really feel the distinction. If such a rise is sustained for a very long time, it could result in a warmth wave.”
Droughts have been a most urgent and protracted downside in Kenya. Way back to 1975, drought cycles used to happen each 10 years. However as local weather change escalates in each frequency and depth, the drought cycle diminished from each 10 years to each 5 years, to each two to 3 years.
Annually there may be an annual dry spell and a meals scarcity and the regularity of extraordinarily dry durations makes it troublesome for the nation to get well from one drought to the subsequent.

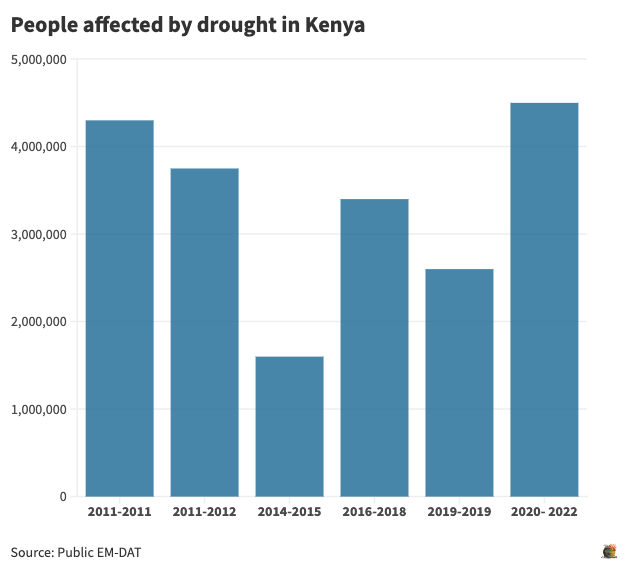
A Historical past of Drought Cycles in Kenya From 1991 to 2020
Drought is an everyday incidence in Kenya. In 1991–1992, greater than 1.5 million individuals have been affected by drought. This was adopted by one other cycle of widespread drought in 1995–1996 that affected at the very least 1.4 million individuals.
In January 1997, the federal government declared drought a nationwide catastrophe, affecting greater than two million individuals, and the famine continued into 1998. Shortly after, in 1999–2000, an estimated 4.4 million individuals have been in dire want of meals assist as a result of a extreme famine. So far as pure disasters go, this was declared the worst within the previous 37 years.
The 1998–2000 drought price the nation an estimated USD 2.8 billion, and this was largely as a result of crops and livestock loss, forest fires, harm to fisheries, diminished hydropower era, diminished industrial manufacturing and diminished water provides.
In 2004, failure of the March to June lengthy rains led to a extreme drought that left greater than three million Kenyans in want of pressing meals assist. In December 2005, the federal government declared drought a nationwide disaster, affecting at the very least 2.5 million individuals in northern Kenya alone.
The drought in 2008 affected 1.4 million individuals and an general 10 million individuals have been prone to starvation after an unsuccessful harvest as a result of drought in late 2009 and into early 2010. The extreme and extended drought brought about the nation USD 12.1 billion in damages and losses, and price over USD 1.7 billion in restoration.
There are 47 counties in Kenya. As solely 20 p.c of Kenya receives excessive and common rainfall, Kenya’s arid and semi-arid (ASAL) areas comprise 18 to twenty of the poorest counties, that are significantly in danger from elevated aridity and durations of drought.
ASAL areas have endured three considerably extreme droughts from 2010 to 2020. The 2010–2011 interval was extreme and extended, affecting at the very least 3.7 million individuals, inflicting USD 12.1 billion in damages and losses, and costing over USD 1.7 billion in restoration and reconstruction wants.
That cycle was adopted by the 2016–2017 drought. The 2020–2022 famine, which was probably the most extreme, longest and widespread as greater than 4.2 million individuals, or 24 p.c of the ASAL inhabitants have been going through excessive ranges of acute meals insecurity.

Overview of Pure Catastrophe Occasions in Kenya, 1991–2020
Kenya is more and more enduring durations of intense, heavy rainfall. Throughout this era, there have been a complete of 45 flood occasions, immediately affecting greater than 2.5 million individuals and inflicting an estimated harm of USD 137 million. These occasions happened in 1997, 1998, 2002, 2012 and 2020, as they have been quick, frequent and intense.
In contrast to drought and famine, Kenya’s historical past with floods is way shorter. There have been many consecutive drought seasons from 1991 to 1997. From 1997, a sample of floods begun to emerge on this East African nation.
It began with the historic extreme and lethal El Nino floods in 1997–1998 that have been widespread and affected 1.5 million individuals. This was adopted by the 2002 floods, that affected 150,000 individuals. Kenya has skilled flooding nearly yearly from 2010 to 2020.

Projected Danger Shifting Ahead
“From 2020 to 2050, projections present that ASAL areas will proceed to obtain lowering rainfall. Temperatures within the nation will proceed to rise by 1.7 diploma Celsius by 2050 and even increased by roughly 3.5 diploma Celsius earlier than the tip of this century. The escalation in local weather change will enhance our local weather danger,” Mildred Nthiga, a local weather change impartial researcher in East Africa, tells IPS.
“We may have much more frequent and damaging floods, and this shall be adopted by longer durations of drought. We now have already began to expertise some worrisome landslides and mudslides and, this can change into a good larger concern, particularly within the highlands.”
Stressing that further soil erosion and water logging of crops will considerably have an effect on agricultural productiveness, decreasing yields and growing meals safety. There may also be vital financial losses, extreme harm to farmlands and infrastructure.
Worse nonetheless, as already witnessed within the latest 2024 lethal floods—human causalities. This may deepen rural poverty and starvation, and derail Kenya’s progress in the direction of attaining the UN’s Sustainable Growth Targets.
Word: This function is revealed with the help of Open Society Foundations.
IPS UN Bureau Report
Comply with @IPSNewsUNBureau
Comply with IPS Information UN Bureau on Instagram
© Inter Press Service (2024) — All Rights ReservedAuthentic supply: Inter Press Service