Following the 7 October 2023 Hamas assaults, Israel’s army operations in Gaza and their humanitarian penalties have introduced the query of commerce sanctions on Israel into public debate. As of July 2024, Israel’s offensive has resulted within the deaths of over 37,000 Palestinians. This quantity might rise to over 186,000 when contemplating oblique deaths as a consequence of, amongst different components, destroyed health-care infrastructure or meals and water shortages. Seventy per cent of Gaza’s homes have been destroyed, and eighty per cent of the inhabitants has been displaced. In response, Turkey has suspended commerce whereas different international locations, together with Belgium, Canada, Italy, Japan, the Netherlands and Spain, have determined to stop arms commerce. In Europe, governments in Belgium, Eire and Spain have publicly advocated for the implementation of commerce sanctions. The problem has additionally been raised within the European Union’s International Affairs Council.
Financial sanctions have turn out to be a outstanding instrument in modern international coverage. As of 2023, the UN manages 14 ongoing sanctions, whereas america has imposed over 25 because the early 2000s. Analysis on their effectiveness means that financial sanctions are usually simpler after they impose substantial financial prices on the goal financial system, are multilateral and led by worldwide establishments, goal for reasonable coverage adjustments fairly than bold objectives, goal allies fairly than adversaries, and are directed at democratic regimes.
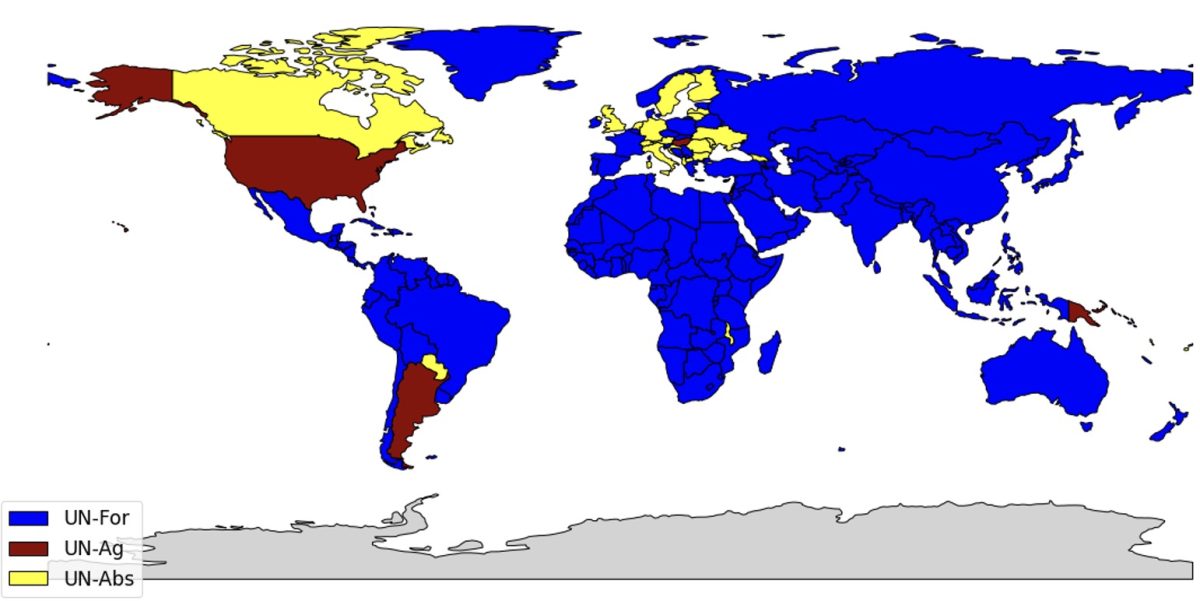
On this evaluation, I take advantage of a multi-country, multi-sector mannequin of commerce to look at the results of tariff sanctions on Israel. The mannequin relies on De Souza et al (2024), Caliendo and Parro (2015) and Ossa (2014). Corporations in every nation competitively produce tradable items in numerous sectors which might be used each for remaining consumption and as manufacturing components alongside labor and intermediate inputs. Commerce is topic to iceberg prices in addition to import and export tariffs set by governments. I calibrate the mannequin utilizing the OECD Inter-Nation Enter-Output desk, a dataset that describes the interdependencies between 45 financial sectors and 76 international locations. I classify international locations into 4 teams primarily based on their vote on decision (A/ES-10/L.30/Rev.1) for Palestine’s admission to the UN: Israel, international locations that voted in opposition to the decision (abbreviated “UN-Ag”, 9 international locations together with america, Argentina, Hungary), international locations that voted for the decision (abbreviated “UN-For”, 143 international locations together with China, France, Japan), and international locations that abstained (abbreviated “UN-Abs”, 25 international locations together with the UK, Germany, Italy, Canada). Determine 1 presents a map of nations primarily based on their completely different votes.
I assume that the sanctioning international locations are these within the “UN-For” group. I acknowledge that this assumption includes a big diploma of arbitrariness. The query of which international locations usually tend to impose sanctions is past the scope of this evaluation. The target right here is fairly to judge the results of such sanctions. I’ve in contrast this group with different hypothetical coalitions of sanctioning international locations: the European Union, the BRICS (Brazil, Russia, India, China, South Africa), and america. Lastly, whereas I focus right here on the financial penalties of import and export tariffs, financial sanctions will also be applied by means of numerous different means, together with asset freezes, sanctions on monetary markets, or entry restrictions for key authorities officers and enterprise executives.
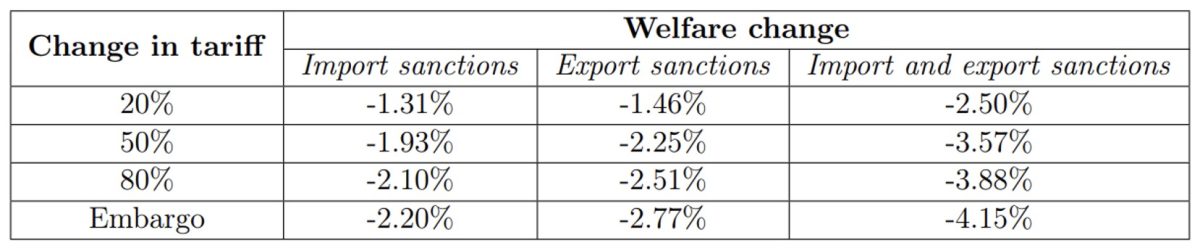
The outcomes, displayed in Desk 1, present that export tariffs would have barely extra affect than import tariffs. With a 20% change in import tariff, Israel’s gross nationwide revenue (GNI) would lower by 1.31%, and as much as 2.20% with a ban on imports. For a 20% change in export tariff, the lower can be of 1.46%, and be 2.77% with an export ban. When the 2 measures (import and export tariffs) are mixed, the lower ranges from 2.50% (20% tariff) to 4.15% (commerce embargo). Lastly, in all situations, the affect of sanctions on different international locations (each sanctioning and non-sanctioning) is negligible, round -0.02%. Which means there is no such thing as a financial trade-off concerning the extent of tariffs: it’s a political alternative.
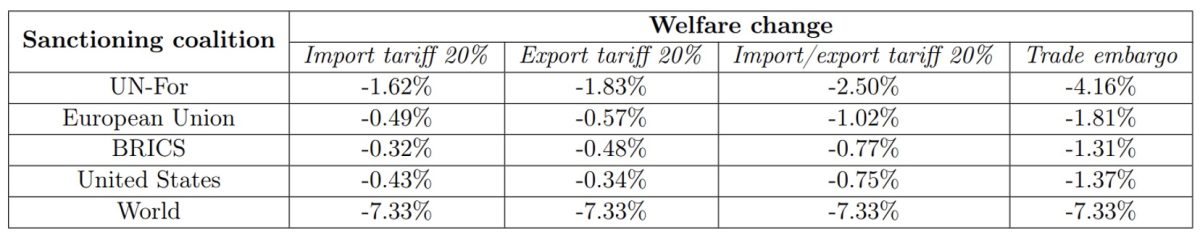
Desk 2 compares the outcomes for various coalitions of sanctioning international locations. A rise in import and export tariffs by 20% from the European Union would cut back Israel’s GNI by 1.02%. The identical improve from the BRICS would cut back it by 0.77%, roughly the identical as america (0.75%). For comparability, the affect of a commerce embargo from the EU can be -1.81%, from the BRICS -1.31% and from america -1.37%. On the excessive, if all international locations of the world have been concerned in a commerce embargo, the affect can be -7.33%. This exhibits that the bigger the coalition imposing sanctions, the extra vital the financial affect.
These values are throughout the vary of Neuenkirch and Neumeier (2015), who estimate the affect of “extreme” UN sanctions, comparable to full embargos imposed by UN member states in opposition to a goal nation, on the order of -5% to -6% on GDP development. They’re additionally according to Armington mannequin’s predictions that the welfare features from commerce ought to be at the least equal to 1 − λ−1/ε, the place λ is one minus the import penetration ratio and ε is the commerce elasticity. Israel’s import penetration ratio is 17%, therefore λ = 0.83, commerce elasticity is round -5, implying welfare losses from embargo to be at the least 3.66%.
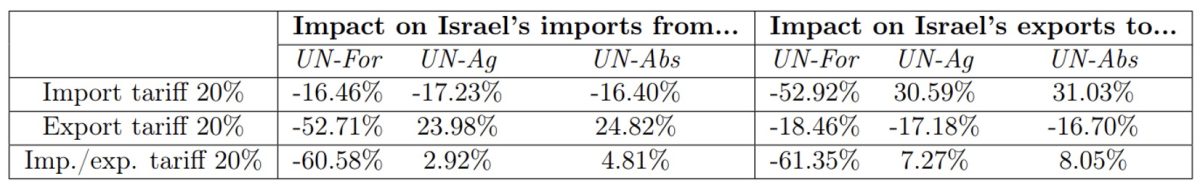
Desk 3 shows the impact of sanctions on commerce between Israel and different international locations. The imposition of a 20% import (resp. export) tariff by UN-For would cut back Israel’s export to (resp. import from) these international locations by 52.92% (resp. 52.71%). It could partially be offset by a rise in Israel’s exports to (resp. imports from) non-sanctioning international locations: 30.59% to UN-Ag, 31.03% to UN-Abs (resp. 23.98% from UN-Ag, 24.82% from UN-Abs).
I now research the breakdown of the results of commerce sanctions by sector. I assume that sanctioning international locations impose a 20% improve in import and export tariffs, and that Israel doesn’t impose any counter-sanctions. I additionally assume no sanctions on meals and pharmaceutical merchandise.
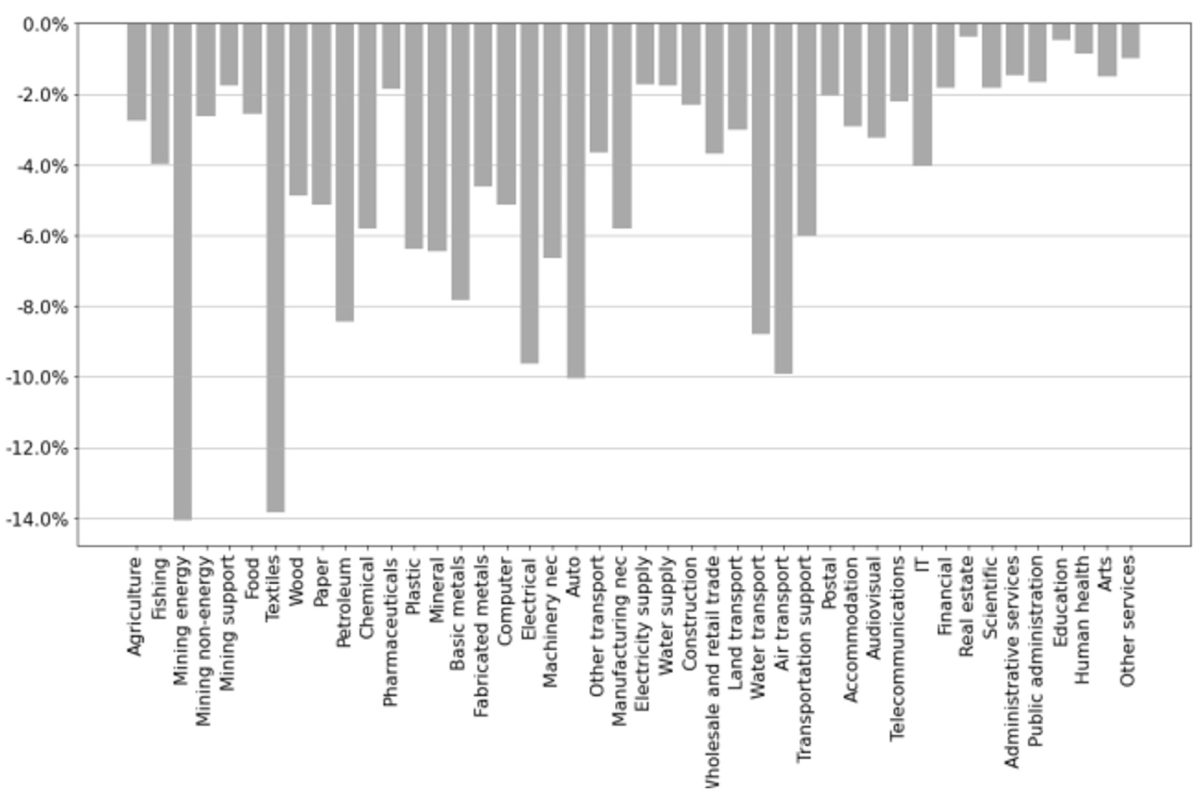
Determine 2 illustrates the change in buying energy of wage (PPW) throughout numerous sectors. It reveals how a lot the amount of products or companies that may be purchased with a unit of wage adjustments in every sector because of the sanctions. The sectors experiencing probably the most vital lower in PPW are fossil fuels (-14.07%) and textiles (-13.83%). Refined petroleum (-8.43%) can be notably affected because of the affect on fossil fuels. Different sectors exhibiting appreciable declines embrace vehicles (-10.06%), air transport (-9.92%) and electrical gear (-9.63%). The consequences on important items, comparable to meals (-2.58%), prescription drugs (-1.85%), and electrical energy (-1.73%), stay reasonable.
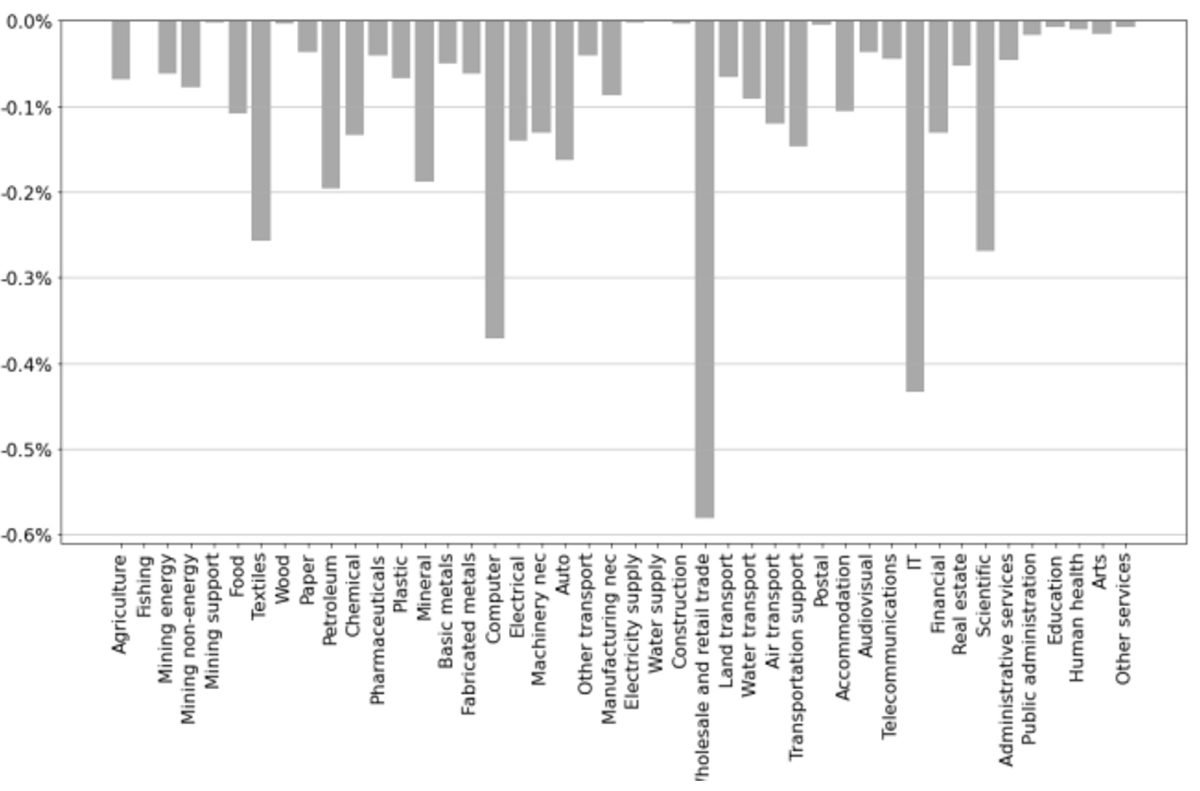
I lastly study which sectors are the simplest targets for sector-specific sanctions. Determine 3 illustrates the adjustments in Israel’s GNI ensuing from a commerce embargo in every sector. The sectors the place focused sanctions can be only embrace wholesale and retail commerce, data applied sciences (IT), computer systems, and scientific companies. These final three sectors emphasize Israel’s reliance on its high-tech financial system. As of 2022, the high-tech sector constituted 18.1% of Israel’s GDP, a 4 share level improve from 2012, making it the main sector within the nation’s financial system. Excessive-tech additionally accounted for 48.3% of Israel’s exports, a determine that has greater than doubled over the previous decade.
The outcomes of this research point out that tariff sanctions might have vital results on Israel’s gross nationwide revenue. Sanctions are discovered to be simpler after they contain a lot of sanctioning international locations and after they goal high-tech services and products.
Tables and Figures
Determine 1: Map of nations primarily based on their vote on decision (A/ES-10/L.30/Rev.1) for the admission of Palestine as a UN member state.
Determine 2: Change in buying energy of wage by sector.
Determine 3: GNI affect of sector-specific commerce embargo by sector.
Desk 1: Change in Israel’s gross nationwide revenue for numerous tariff adjustments.
Observe: Import sanctions correspond to a rise in import tariffs by the sanctioning coalition. Export sanctions correspond to a rise in export tariffs by the sanctioning coalition.
Desk 2: Change in Israel’s gross nationwide revenue for numerous sanctioning coalitions.
Desk 3: Influence of tariff sanctions on Israel’s imports and exports.
Additional Studying on E-Worldwide Relations












